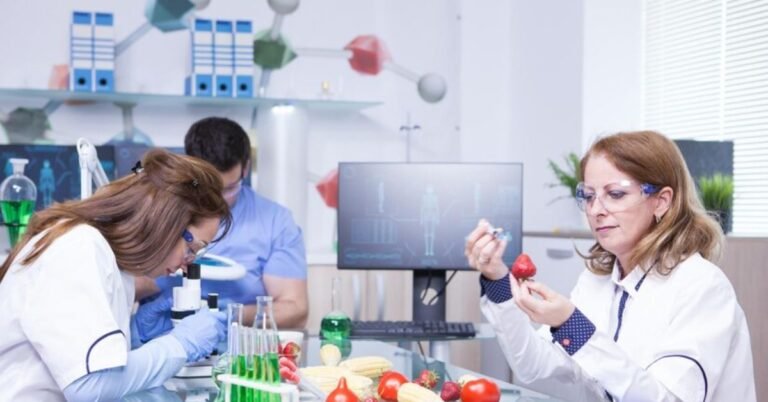
Clinical trials are not merely a step in drug development; they form the backbone of modern healthcare advancements, shaping the future of medical treatment. Many often contemplate the pros and cons of taking part in clinical trial activities. This contemplation is crucial, as understanding these trials’ profound impact on individual and public health can help demystify them. Serving as a bridge between laboratory research and patient care, clinical trials validate new interventions and translate scientific discoveries into therapeutic realities.
Clinical Trials: An Overview
Clinical trials are crucial research activities to evaluate new medical, surgical, or behavioral interventions. They form a pivotal part of medical research, providing the evidence required to validate the safety and effectiveness of new treatments and determine their role in patient care. Typically conducted in carefully controlled environments, these trials are guided by stringent scientific protocols to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the results. They are fundamental in advancing medical knowledge and guiding health policies and regulatory decisions that uplift the quality of care worldwide.
The Importance of Clinical Trials in Healthcare
Clinical trials are central to advancements in medicine. They offer vital insights into the therapeutic potential of new treatments, thus determining whether these medical advancements can be incorporated into everyday healthcare practices. Through rigorous testing processes, clinical trials authenticate the efficacy of new drugs, medical devices, and treatment protocols, ensuring they are safe for human use. The data collected during these trials influence treatment guidelines and healthcare policies globally. Moreover, they are instrumental in uncovering new indications for existing treatments, thereby expanding therapeutic options for patients with unmet medical needs.
Stages of Clinical Trials: From Concept to Approval
Clinical trials unfold through multiple meticulously planned phases, each contributing uniquely to assessing a treatment’s viability. Phase I trials are essential in evaluating a drug’s initial safety and pharmacokinetics in a small group of healthy volunteers or patients, establishing the groundwork for all subsequent research. Phase II trials expand on this by providing preliminary data on efficacy while continuing to assess safety, often involving a larger group of participants. Phase III trials are conducted on a broader scale, sometimes across multiple locations, to confirm efficacy and monitor side effects in a diverse patient population. Finally, Phase IV trials, or post-marketing studies, gather additional data on a treatment’s risk-benefit profile as real-world use expands, leading to improved recommendations and potentially revealing rare long-term effects. Each phase is critical in ensuring that only the most effective and safe therapies reach patients.
Benefits of Participating in Clinical Trials
Participating in clinical trials offers numerous advantages, both for individual participants and society at large. For participants, trials frequently provide access to novel therapies before they become publicly available, especially significant for those battling conditions with limited treatment options. Involvement in a trial typically includes access to superior healthcare services and regular check-ups, thanks to a group of skilled healthcare experts committed to delivering individualized care and tracking health results. Additionally, involvement in these trials contributes to the broader scientific community by helping to generate data essential for advancing medical research. This altruistic contribution aids in discovering groundbreaking treatments that may benefit countless individuals in the future, underlining the collaborative spirit and shared humanity at the heart of medical research.
Common Misconceptions About Clinical Trials
Despite their importance, clinical trials are often surrounded by myths and misconceptions. One prevalent myth suggests that participants are used as mere ‘guinea pigs’ without appropriate safeguards. It is far from reality, as robust ethical and regulatory frameworks are entrenched in clinical trial protocols, prioritizing participant safety and informed consent. Another common fear is the likelihood of receiving a placebo instead of an active treatment. While placebos play a role in some trials, primarily to assess the efficacy of non-critical interventions, ethical standards ensure that trials involving life-threatening conditions offer new therapies alongside the best current standard of care, not placebos. Addressing these misconceptions is vital to improving public understanding and encouraging informed, voluntary participation in clinical research.
The Future of Clinical Trials
The realm of clinical trials is set for significant transformations, hinting at a future full of innovation. Technological advancements are revolutionizing how trials are designed and conducted, facilitating more robust data analysis and reducing the time required for trial completion. Decentralized trials, leveraging digital platforms, enhance trial accessibility and participant convenience by eliminating geographic barriers. Furthermore, precision medicine, powered by genomic insights, tailors therapies to individual patient profiles, promising higher efficacy and fewer side effects. All these trends are converging to reshape clinical trial methodologies, promoting more personalized and efficient research outcomes.
How to Get Involved in Clinical Trials
For individuals keen on joining clinical trials, maneuvering through the field demands knowledgeable and tactical methods. Begin by researching active trials on platforms that list comprehensive details on inclusion criteria, study design, and trial objectives. Potential participants need to thoroughly understand the possible risks and benefits associated with trial involvement. Consulting with healthcare providers can provide personalized guidance and ensure participation aligns with overall health goals. Engaging in such open dialogue ensures a thoughtful decision-making process and underscores the participant’s proactive role in advancing healthcare advancements.
Resources for Learning More
Numerous educational resources richly support the journey toward understanding clinical trials. The National Institutes of Health is an authoritative source, offering information on trial procedures, participant safety, and the broader impact of clinical research on healthcare. Exploring such resources empowers individuals with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions about trial participation and showcases clinical trials’ profound impact on advancing medical science. With this information, prospective participants can actively contribute to the shared mission of enriching and transforming global healthcare paradigms.